Lead-acid batteries are a popular type of rechargeable battery that have been used for decades. They are widely employed in various applications, ranging from automotive and marine industries to telecommunications and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS). In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the functionality, working principle, types, and advantages of lead-acid batteries.
How Lead-Acid Batteries Work
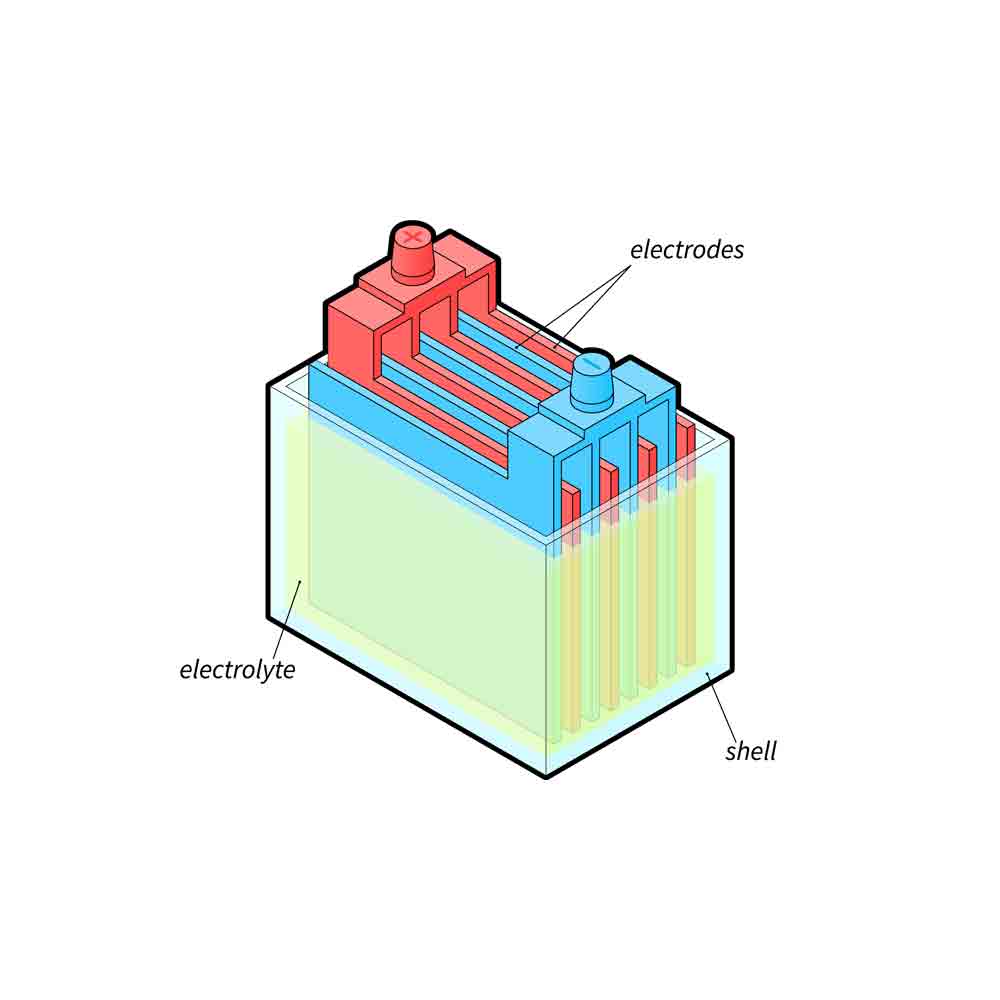
Lead-acid batteries operate based on a simple chemical reaction between lead and sulphuric acid. The battery consists of two electrodes, a positive electrode (known as the anode) and a negative electrode (known as the cathode). These electrodes are immersed in an electrolyte solution of sulphuric acid.
When the battery discharges, the sulphuric acid reacts with the lead in the positive electrode, resulting in the release of electrons. This process generates electrical energy that can be used to power various devices. As the battery discharges further, the sulphuric acid migrates to the negative electrode and reacts with the lead, creating lead sulphate and water.
During the charging process, the chemical reaction is reversed. An external source of electricity is applied to the battery, causing the lead sulphate to convert back into lead and sulphuric acid. This restores the battery’s capacity and allows it to be reused.
 Types of Lead-Acid Batteries
Types of Lead-Acid Batteries
There are several types of lead-acid batteries, each designed for specific applications:
- Starting, Lighting, and Ignition (SLI) Batteries: These batteries are commonly used in vehicles, providing the necessary power to start the engine, power the lights, and operate other electrical systems.
- Deep-Cycle Batteries: Deep-cycle batteries are designed to provide a steady amount of power over an extended period. They are often used in renewable energy systems, golf carts, forklifts, and marine applications.
- Valve-Regulated Lead-Acid (VRLA) Batteries: VRLA batteries are maintenance-free and sealed, making them suitable for applications where regular maintenance is not feasible. They are commonly used in telecommunications, emergency lighting, and UPS systems.
- Flooded Lead-Acid Batteries: These batteries require periodic maintenance and are commonly found in older vehicles and industrial applications.
- Applications of Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries find applications in various industries and sectors:
- Automotive: Lead-acid batteries are extensively used in automobiles, providing the necessary power to start the engine and operate the vehicle’s electrical systems.
- Telecommunications: Lead-acid batteries are crucial for providing backup power to telecommunication systems, ensuring uninterrupted communication during power outages.
- Renewable Energy: Lead-acid batteries play a vital role in storing energy generated from renewable sources such as solar and wind, allowing for a continuous power supply.
- Industrial: Lead-acid batteries are used in industries forklifts, emergency lighting, uninterrupted power supplies, and backup power systems.
What gas is produced when charging a lead acid battery
When charging a lead-acid battery, the gas primarily produced is hydrogen (H2). This gas is a byproduct of the electrochemical reaction that occurs during the charging process. The charging process involves the conversion of lead sulfate (PbSO4) back into lead (Pb) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4). As the charging current passes through the battery, electrolysis takes place, causing the water (H2O) molecules in the electrolyte to split into hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide ions (OH-). The hydrogen ions then combine to form hydrogen gas, which is released as a result of the charging process. It’s important to note that the release of hydrogen gas during charging should be done in a well-ventilated area, as hydrogen gas is highly flammable.
Advantages of Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries offer several advantages that make them a preferred choice in various applications:
- Cost-Effective: Lead-acid batteries are relatively inexpensive compared to other battery technologies, making them cost-effective for many industries.
- Robust and Reliable: These batteries are known for their durability and ability to withstand extreme conditions, making them suitable for demanding environments.
- High Energy Density: Lead-acid batteries offer high energy density, allowing for efficient energy storage and prolonged power supply.
- Recyclability: Lead-acid batteries are highly recyclable, with a well-established recycling infrastructure that helps minimize environmental impact.
Lead-acid batteries are a versatile and reliable energy storage solution used in a wide range of applications. Their long-standing presence in the market, cost-effectiveness, and recyclability continue to make them a popular choice across various industries. Understanding the functionality, types, and advantages of lead-acid batteries is essential for anyone seeking efficient and dependable power storage solutions.
Comments are closed.





